What is Remote vs Local Mail Exchanger?
What is Remote vs Local Mail Exchanger? Remote and local mail exchangers refer to different configurations for handling email delivery in a network environment, typically associated with mail servers.
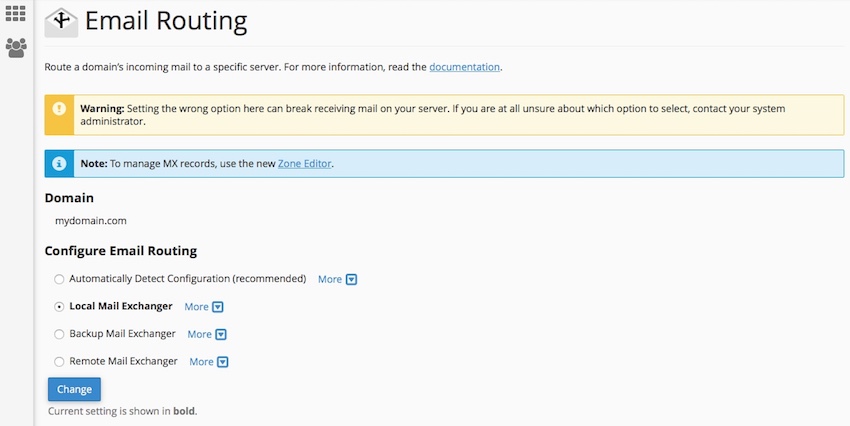
What is Remote vs Local Mail Exchanger?
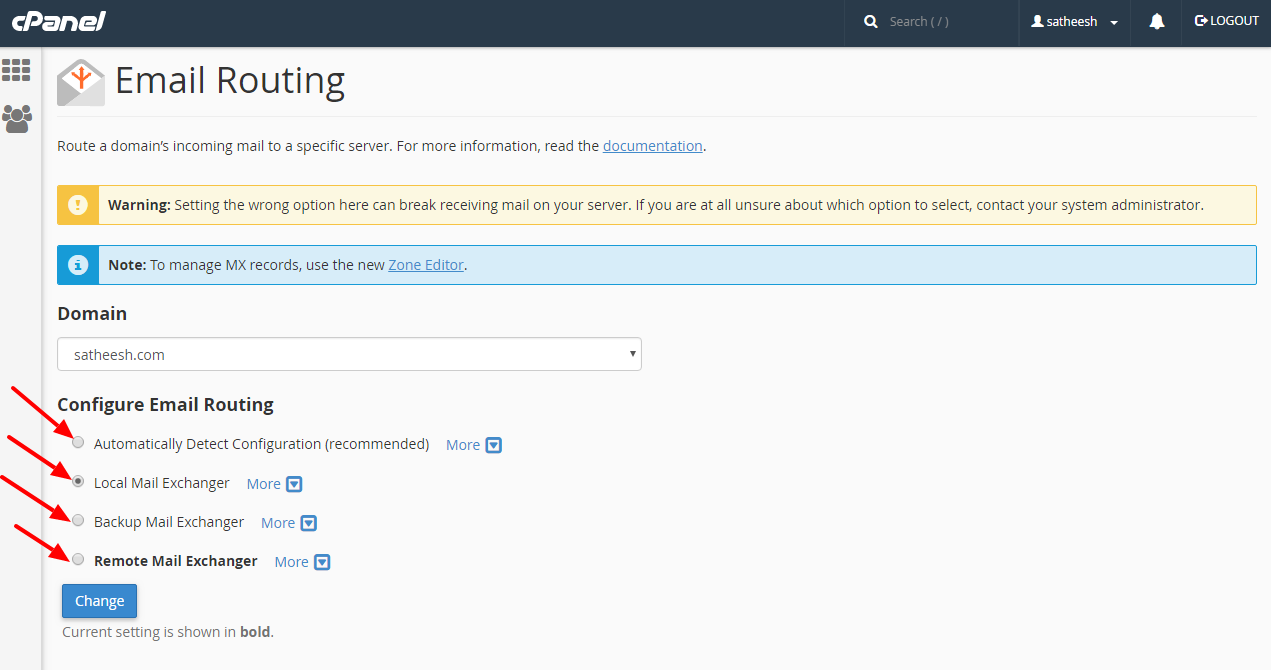
- Local Mail Exchanger (MX):
- A local mail exchanger refers to a mail server that is designated to handle email delivery for a particular domain within the same network or organization.
- When a mail server is configured as a local mail exchanger for a domain, it means that any email addressed to users within that domain will be routed directly to this mail server.
- The local mail exchanger stores and manages the mailboxes for users on that domain, allowing them to send, receive, and store email messages.
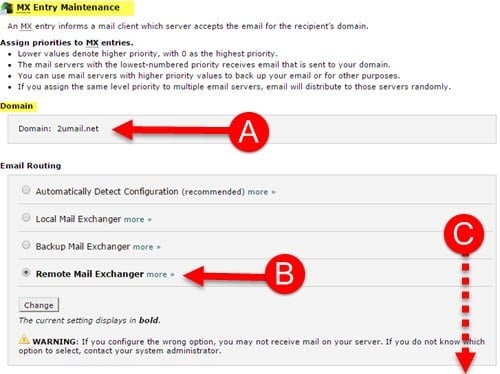
What is Remote vs Local Mail Exchanger?
- Remote Mail Exchanger (MX):
- A remote mail exchanger, on the other hand, is a mail server that is designated to handle email delivery for a domain but is located outside of the domain’s immediate network or organization.
- When a mail server is configured as a remote mail exchanger for a domain, it means that email addressed to users within that domain will be routed externally to this mail server.
- The remote mail exchanger then forwards these emails to the appropriate internal mail servers or directly delivers them to the recipients, depending on how the email routing is configured.
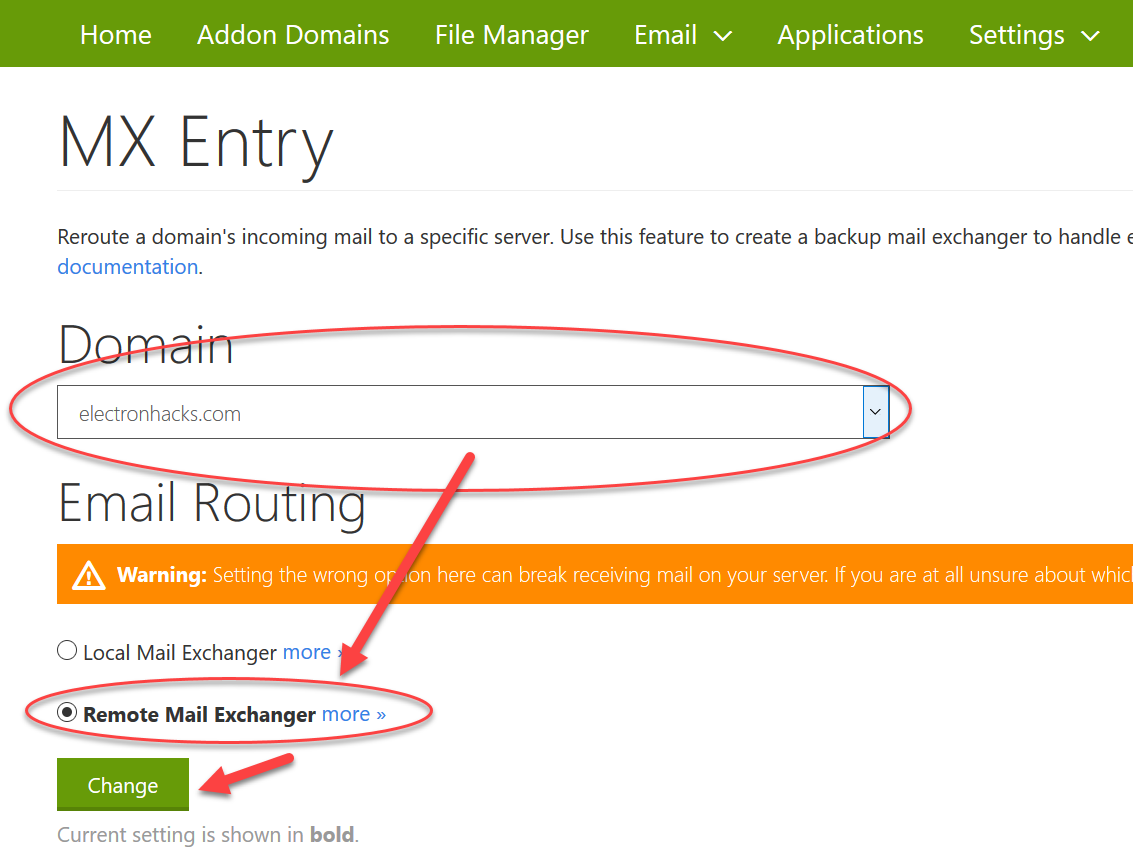
Key Differences:
- Location: Local mail exchangers are within the same network or organization as the domain they handle, while remote mail exchangers are located outside.
- Function: Local mail exchangers manage all aspects of email delivery, including storage and retrieval for local users. Remote mail exchangers primarily handle routing and delivery of emails to the local mail exchanger or directly to recipients.
- Configuration: Local mail exchangers require internal network configuration to handle email traffic efficiently. Remote mail exchangers require proper DNS (Domain Name System) records to ensure correct routing of email traffic from external sources.
In practice, organizations may use a combination of local and remote mail exchangers to optimize email delivery based on their infrastructure, security, and redundancy requirements.
