What is Cloud Hosting? Benefits and Risks
Definition: Cloud hosting is a type of web hosting service that utilizes virtualized resources from multiple servers. It enables users to host their websites or applications on a network of interconnected servers, often referred to as the cloud. The resources, such as computing power, storage, and bandwidth, are distributed across these servers, providing flexibility and scalability.
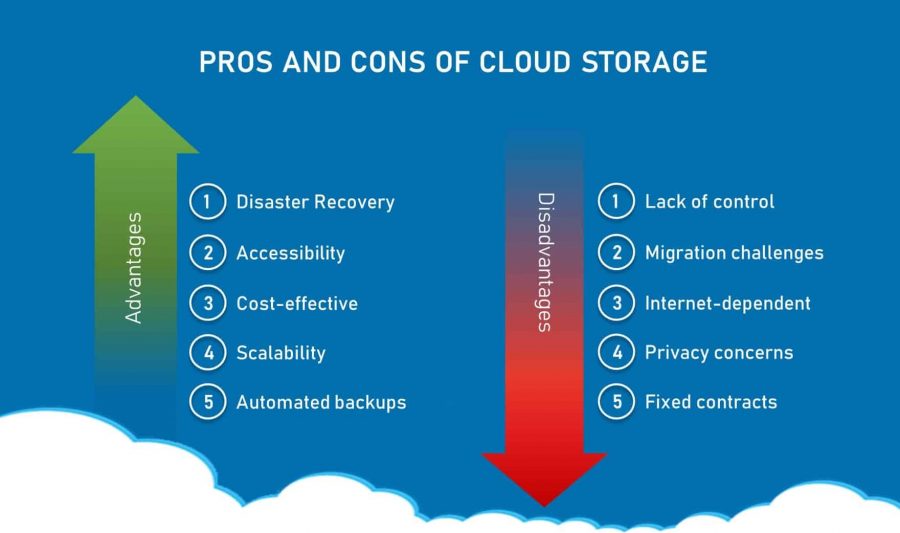
Benefits of Cloud Hosting:
- Scalability:
- Easily scale resources up or down based on demand. This flexibility allows businesses to adapt to changing needs without the need for significant infrastructure changes.
- Reliability and Uptime:
- Cloud hosting services often have redundant systems and backups, minimizing downtime. The distributed nature of the cloud ensures that if one server fails, others can take over seamlessly.
- Cost-Efficiency:
- Pay-as-you-go or subscription-based pricing models allow users to pay only for the resources they consume. This can be more cost-effective than traditional hosting, especially for variable workloads.
- Resource Efficiency:
- Resources are distributed dynamically, allowing for efficient utilization. Users can allocate resources based on their requirements, avoiding over-provisioning or underutilization.
- Global Accessibility:
- Cloud hosting enables users to access their data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. This global accessibility is particularly beneficial for businesses with distributed teams or a diverse user base.
- Automatic Updates:
- Cloud hosting providers often handle server maintenance, updates, and security patches. This frees users from the responsibility of managing these tasks, ensuring a more secure and up-to-date hosting environment.
- Security Measures:
- Reputable cloud providers implement robust security measures, including data encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. This enhances the overall security posture of hosted applications and data.
- Data Redundancy:
- Cloud hosting typically involves storing data across multiple servers and locations. This redundancy helps protect against data loss due to hardware failures or other unforeseen events.
Risks and Considerations:
- Security Concerns:
- While cloud providers invest heavily in security, concerns about data breaches and unauthorized access persist. Users must implement additional security measures and adhere to best practices.
- Dependency on Internet Connection:
- Cloud hosting relies on an internet connection. If the internet connection is lost or experiences latency issues, it can impact the accessibility and performance of hosted applications.
- Data Privacy and Compliance:
- Depending on the geographical location of data centers, users may need to navigate complex data privacy and compliance regulations. Understanding and adhering to these regulations is crucial.
- Limited Customization:
- Some cloud hosting services may have limitations on customization compared to dedicated servers. Businesses with highly specialized requirements may find these limitations restrictive.
- Cost Overruns:
- While the pay-as-you-go model can be cost-effective, it’s important to monitor resource usage to avoid unexpected costs. Uncontrolled resource scaling can lead to budget overruns.
- Vendor Lock-In:
- Users may face challenges if they want to migrate their applications or data from one cloud provider to another. This potential vendor lock-in should be considered when choosing a cloud hosting solution.
- Downtime and Outages:
- While cloud providers strive for high availability, downtime and outages can still occur. Users should be aware of their provider’s service level agreements (SLAs) and plan accordingly.
- Limited Control for Some Users:
- Cloud hosting abstracts much of the underlying infrastructure, which can limit control for users who require deep customization and management of their server environment.
In conclusion, cloud hosting offers numerous benefits, including scalability, reliability, and cost-efficiency. However, potential risks, such as security concerns and dependency on internet connectivity, should be carefully considered. Businesses must weigh the advantages and disadvantages based on their specific requirements and priorities before choosing a cloud hosting solution.
