Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud vs. Hybrid Cloud: Understanding the Differences and Choosing the Right Solution

Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud vs. Hybrid Cloud – In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, cloud computing has become a cornerstone for businesses of all sizes. With its vast potential to streamline operations, improve flexibility, and reduce costs, understanding the different types of cloud environments is crucial for organizations as they determine their best cloud strategy.
When it comes to cloud computing, businesses primarily have three options: Public Cloud, Private Cloud, and Hybrid Cloud. Each of these cloud models offers distinct benefits and trade-offs, and the right choice depends on the organization’s specific needs, budget, and security requirements.
In this blog, we’ll break down each cloud model, compare their key features, and help you make an informed decision based on your business needs.
What is the Cloud?
Before diving into the specifics of each cloud model, it’s essential to understand what “the cloud” means. The cloud refers to servers, storage, and services that are hosted on the internet rather than on a local data center. These cloud services are typically managed by third-party providers, who handle the infrastructure, security, and maintenance, allowing businesses to focus on their core operations.
Now, let’s explore the three main types of cloud models:
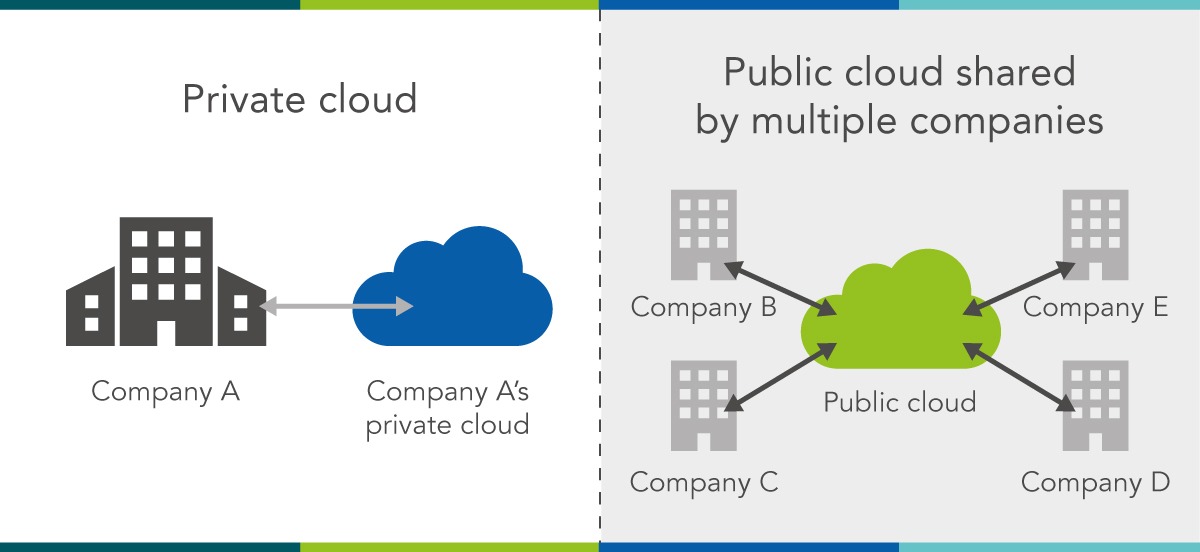
1. Public Cloud
What is Public Cloud?
The Public Cloud is a cloud environment where cloud services—such as computing resources, storage, and networking—are provided by third-party vendors (like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, etc.) and made available to the general public. Resources in a public cloud are shared with other tenants, meaning multiple organizations can use the same infrastructure, though their data is kept separate.
Key Features of Public Cloud:
- Scalability: Public cloud services offer virtually unlimited scalability, meaning you can scale up or down based on demand.
- Cost-Effective: You only pay for what you use, making it a cost-effective choice for organizations that don’t need dedicated resources.
- Maintenance-Free: The cloud provider takes care of hardware and software maintenance, ensuring that the system remains updated and secure.
- Accessibility: Public cloud services are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, offering flexibility and convenience for remote teams.
- Security: While public cloud providers offer robust security protocols, your data shares the infrastructure with other organizations, which could pose security concerns depending on your industry.
Ideal for:
- Startups and Small to Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs) that need cost-effective solutions with the flexibility to scale.
- Businesses with less stringent security and compliance requirements.
- Companies that don’t have the resources or need to maintain their own data centers.
Popular Public Cloud Providers:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- IBM Cloud
2. Private Cloud
What is Private Cloud?
A Private Cloud is a cloud infrastructure that is used exclusively by one organization. It can be hosted on-premises in a company’s data center or by a third-party provider, but the critical difference is that the infrastructure is dedicated solely to that organization. A private cloud allows businesses to enjoy the benefits of cloud computing while maintaining control over their data and resources.
Key Features of Private Cloud:
- Customization: Private cloud environments can be tailored to meet specific business needs, including specialized hardware, configurations, and security protocols.
- Control and Security: Since the cloud is dedicated to one organization, there’s greater control over security, compliance, and data governance. This is especially important for industries with strict regulatory requirements (e.g., finance, healthcare).
- Performance: With dedicated resources, private clouds can offer better performance, especially for organizations with high workloads or low-latency requirements.
- Cost: Private clouds are more expensive compared to public clouds, as the organization is responsible for the infrastructure, maintenance, and other operational costs.
Ideal for:
- Large enterprises or organizations with specific security and compliance requirements.
- Businesses that deal with sensitive data or have workloads that require high-performance computing.
- Companies that want more control over their IT environment and infrastructure.
Popular Private Cloud Providers:
- VMware Cloud
- Oracle Private Cloud
- Microsoft Azure Stack (for hybrid solutions)
3. Hybrid Cloud
What is Hybrid Cloud?
A Hybrid Cloud combines elements of both public and private clouds. It allows organizations to use a mix of on-premises, private cloud resources, and third-party, public cloud services. This model enables businesses to run critical workloads on private infrastructure while utilizing the public cloud for less-sensitive tasks or for scaling up during periods of high demand.
Key Features of Hybrid Cloud:
- Flexibility: Hybrid cloud offers flexibility by allowing businesses to shift workloads between private and public clouds based on their needs.
- Cost Optimization: Organizations can optimize costs by using the private cloud for sensitive workloads and the public cloud for variable workloads that are cost-effective to scale.
- Disaster Recovery and Backups: A hybrid cloud can be used for backup and disaster recovery by storing backup data in the public cloud, offering greater resilience without the need for a separate infrastructure.
- Security: The hybrid cloud offers enhanced security options by allowing businesses to keep sensitive data in a private cloud, while leveraging the public cloud for less-sensitive applications.
Ideal for:
- Medium to Large Enterprises that need to balance security with scalability.
- Organizations looking to modernize their infrastructure but want to keep certain systems and data on-premises for compliance or operational reasons.
- Businesses with variable workloads, such as e-commerce sites that need to scale during peak traffic times.
Popular Hybrid Cloud Providers:
- Microsoft Azure Hybrid Cloud
- AWS Outposts
- Google Anthos
- VMware Cloud on AWS
Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud vs. Hybrid Cloud – Comparison

1. Cost
- Public Cloud: Most cost-effective, as you only pay for what you use.
- Private Cloud: More expensive due to infrastructure, hardware, and maintenance costs.
- Hybrid Cloud: Typically, a mix of costs—lower than private but higher than public, depending on the extent of the private infrastructure used.
2. Scalability
- Public Cloud: Highly scalable, with almost unlimited capacity.
- Private Cloud: Limited by the physical infrastructure of the organization.
- Hybrid Cloud: Scalable, but requires coordination between public and private environments.
3. Security
- Public Cloud: Good security, but less control over the infrastructure, which may be a concern for sensitive data.
- Private Cloud: Higher security and control over data and infrastructure, ideal for sensitive industries.
- Hybrid Cloud: Offers a balance, enabling sensitive data to remain on a private cloud while leveraging the scalability of public clouds.
4. Customization
- Public Cloud: Limited customization options.
- Private Cloud: High level of customization and control over infrastructure and configurations.
- Hybrid Cloud: Offers customization for both environments, but requires careful management of both private and public resources.
Which Cloud Model is Right for Your Organization?
Choosing the right cloud solution depends on several factors, including your organization’s size, budget, security requirements, and specific workloads. Here’s a quick guide to help you decide:
- Choose Public Cloud if:
- You need a cost-effective, scalable solution.
- You have variable workloads or non-sensitive data.
- You want to offload the management and maintenance of IT infrastructure to a third-party provider.
- Choose Private Cloud if:
- You need full control over your infrastructure.
- You are in a highly regulated industry (e.g., healthcare, finance).
- Security, compliance, and performance are top priorities.
- Choose Hybrid Cloud if:
- You want to keep some workloads on a private cloud and move others to a public cloud.
- You need flexibility to scale resources based on demand.
- You want to optimize costs and improve disaster recovery capabilities.
Conclusion

Public Cloud, Private Cloud, and Hybrid Cloud depends on the unique needs of your organization. While the public cloud offers cost savings and scalability, private clouds give you control, security, and customization. Hybrid clouds provide the best of both worlds, enabling businesses to optimize costs, flexibility, and security.
Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud vs. Hybrid Cloud requirements, and security concerns, you can make an informed decision on which cloud solution will deliver the most value to your organization.
