How to Resolve Common RDP Connectivity Problems
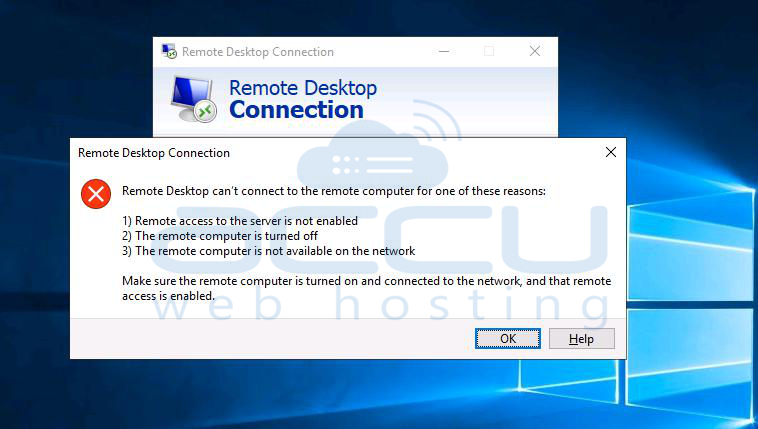
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a powerful tool that allows users to connect to another computer over a network connection. However, users often encounter connectivity issues that can disrupt their workflow. This guide will help you identify and resolve common RDP connectivity problems.
1. Check Network Connection
Ensure Stable Internet Connection:
- Verify that both the client and the host machine have stable internet connections.
- Restart your router or switch to a different network if necessary.
Test Network Connectivity:
- Use the
pingcommand to check connectivity between the client and the host.bash
ping [IP address of the remote machine]
2. Verify RDP Settings
Enable Remote Desktop on Host Machine:
- Go to System Properties on the host machine.
- Select the Remote tab.
- Ensure that Allow remote connections to this computer is selected.
Check Firewall Settings:
- Ensure that the firewall on both the client and the host machine allows RDP traffic.
- For Windows Firewall:
- Go to Control Panel > System and Security > Windows Defender Firewall > Allow an app or feature through Windows Defender Firewall.
- Ensure Remote Desktop is checked for both Private and Public networks.
3. Verify User Permissions
Ensure Proper User Permissions:
- The user account attempting to connect must have permission to access the host machine.
- Go to System Properties > Remote on the host machine.
- Click Select Users and add the necessary user accounts.
4. Check Port Configuration
Default RDP Port:
- Ensure RDP is listening on the default port 3389.
- Use
netstatto verify:bash
netstat -an | find "3389"

Change RDP Port (if necessary):
- Sometimes, changing the RDP port can resolve conflicts.
- Modify the registry to change the RDP port:
- Press
Win + R, typeregedit, and press Enter. - Navigate to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\TerminalServer\WinStations\RDP-Tcp. - Find the
PortNumberkey and change its value.
- Press
5. Update and Restart Services
Restart RDP Services:
- Restart the Remote Desktop Services on the host machine.
bash
net stop termservice
net start termservice
Update RDP Client and Host:
- Ensure that both the client and host machines are running the latest version of RDP.
- Install any pending Windows updates.

RDP Connectivity Problems
6. Address DNS Issues
Flush DNS Cache:
- Sometimes DNS issues can cause connectivity problems.
bash
ipconfig /flushdns
Check DNS Configuration:
- Ensure that the DNS settings on both client and host machines are correct.
- Use public DNS servers (e.g., Google DNS: 8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4) as an alternative.
7. Examine Security Software
Check Antivirus/Antimalware Software:
- Some security software can block RDP connections.
- Temporarily disable antivirus or antimalware software to see if it resolves the issue.
Check Group Policies:
- Sometimes Group Policy settings can affect RDP connectivity.
- Run
gpedit.mscand navigate toComputer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections. - Ensure the policy Allow users to connect remotely using Remote Desktop Services is enabled.
8. Check for Multiple Sessions
Limit Concurrent Connections:
- Ensure that the host machine is not exceeding its allowed number of concurrent RDP sessions.
- Configure session limits in the Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration.
9. Analyze Logs and Error Messages
Check Event Viewer:
- Use Event Viewer to check for detailed error messages.
- Press
Win + R, typeeventvwr, and press Enter. - Navigate to Windows Logs > Application and System to look for RDP-related errors.
- Press
Common Error Messages:
- Error codes and their meanings can provide clues to the underlying problem.
- Example: Error 0x204 typically indicates network issues.
By systematically checking each of these potential issues, you can resolve most common RDP connectivity problems. If problems persist, consider consulting your network administrator or IT support team for further assistance.
